Security
Notes and quick reference
This page is a high-level security reference: common vulnerabilities, typical attack patterns, and terminology. It is intended as a quick overview and reminder for defensive thinking.
Vulnerabilities and attacks
A vulnerability is a weakness in design, implementation, operation, or internal control. Many vulnerabilities are tracked in the CVE ecosystem. An exploitable vulnerability is one for which at least one working exploit exists.
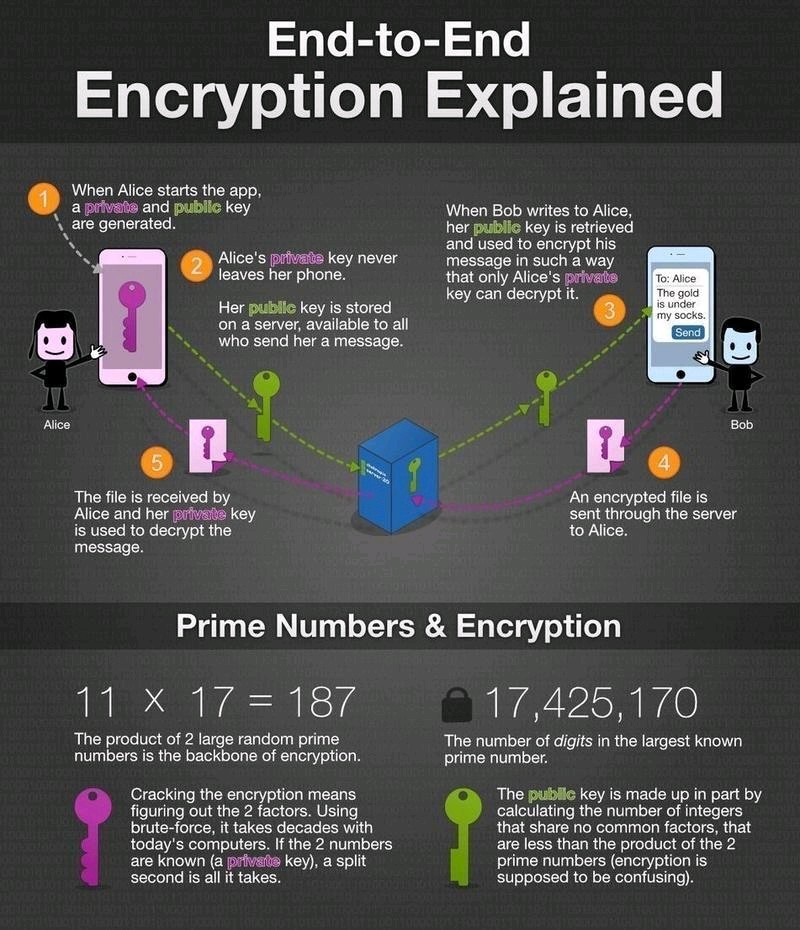
End-to-end encryption
End-to-end encryption means only the communicating endpoints can read the content. Intermediaries can relay traffic, but cannot decrypt the payload.
Backdoor
A backdoor is a hidden method of bypassing authentication or security controls. Backdoors can be intentional or caused by poor configuration, and they create a serious security risk.
Denial-of-service attack (DoS/DDoS)
DoS attacks attempt to make a service unavailable. DDoS attacks distribute the load from many sources, making them harder to block using simple IP-based rules.
Direct-access attacks
Physical access can allow an attacker to copy data or modify the system. Disk encryption and TPM-backed protections can reduce impact, but physical access still raises risk.
Eavesdropping
Eavesdropping is listening to communication traffic (network or otherwise). TLS prevents content visibility, but metadata and endpoints may still leak information.
Phishing
Phishing is social engineering intended to trick people into giving up credentials or sensitive data. Typical delivery vectors are email and messaging platforms, often with fake websites or links.
Privilege escalation
Privilege escalation occurs when an attacker with limited permissions gains higher privileges, such as administrator/root access.
Reverse engineering
Reverse engineering is deconstructing software or systems to understand design, code, or behavior. It is often used in security research and malware analysis.
Social engineering
Social engineering manipulates people to reveal secrets or perform actions. Business email compromise (BEC) is a common example targeting finance workflows.
Spoofing
Spoofing is masquerading as a legitimate entity by falsifying data. Common variants include email spoofing, IP spoofing, MAC spoofing, and biometric spoofing.
Tampering
Tampering is unauthorized modification of data, configurations, or system components. Examples include Evil Maid attacks and device-level manipulation.
Malware
Malware is malicious software designed to gain control, steal data, disrupt systems, or maintain persistence on a host.